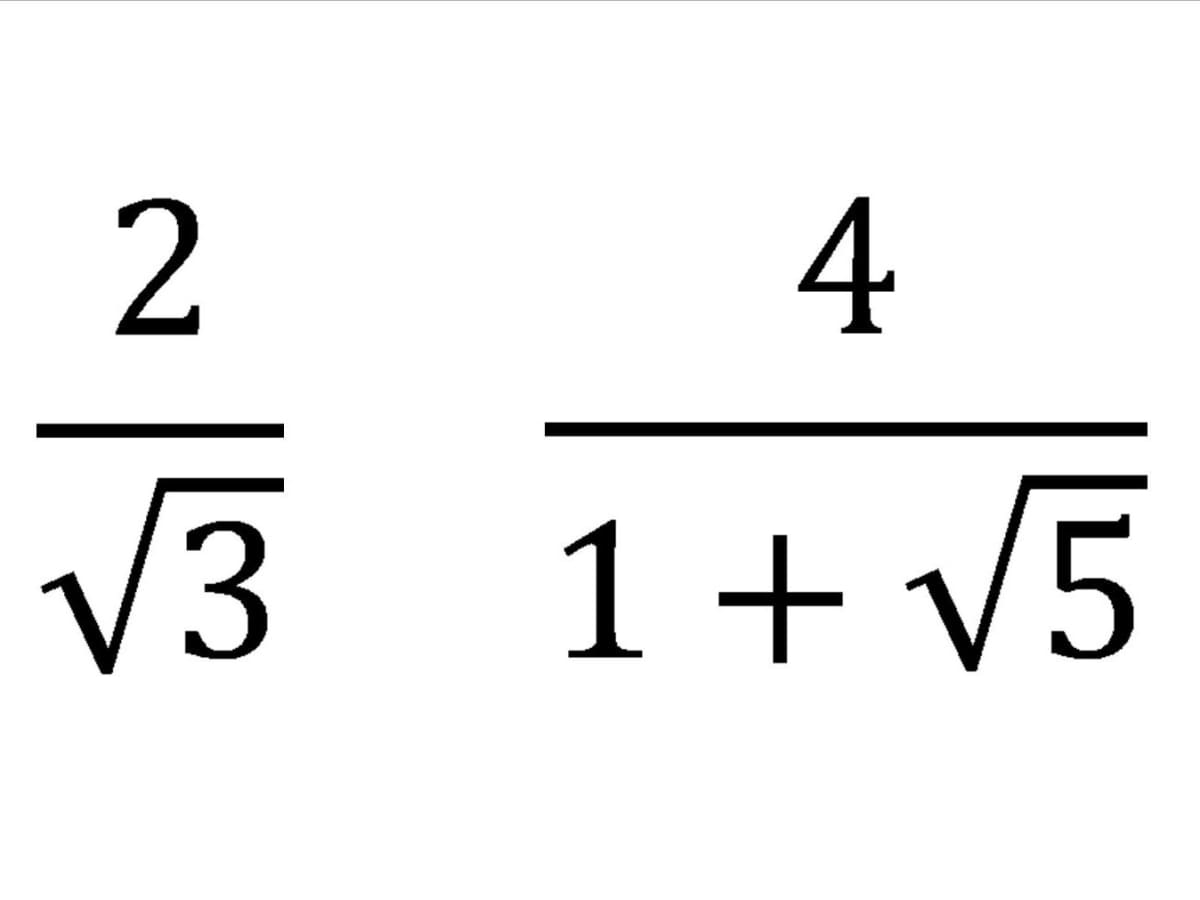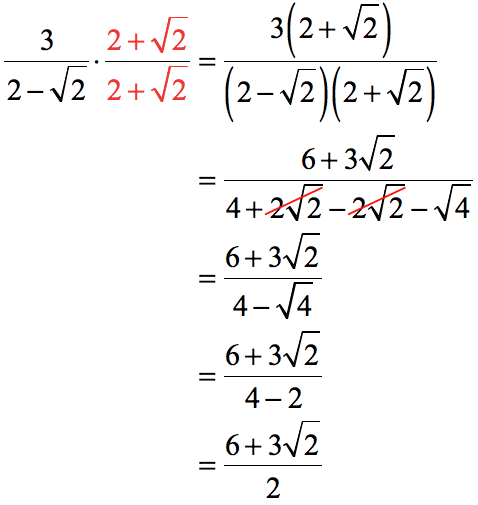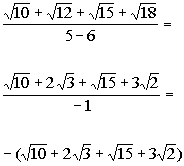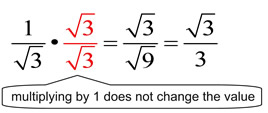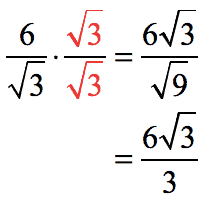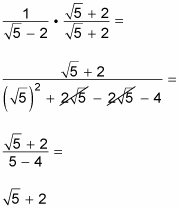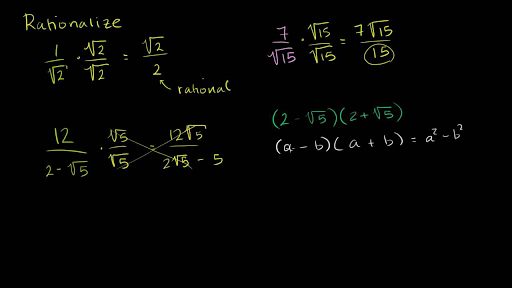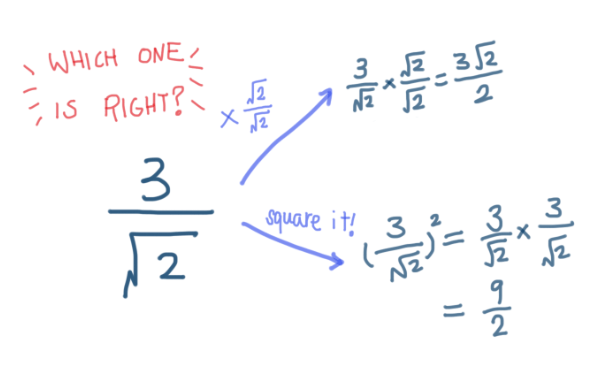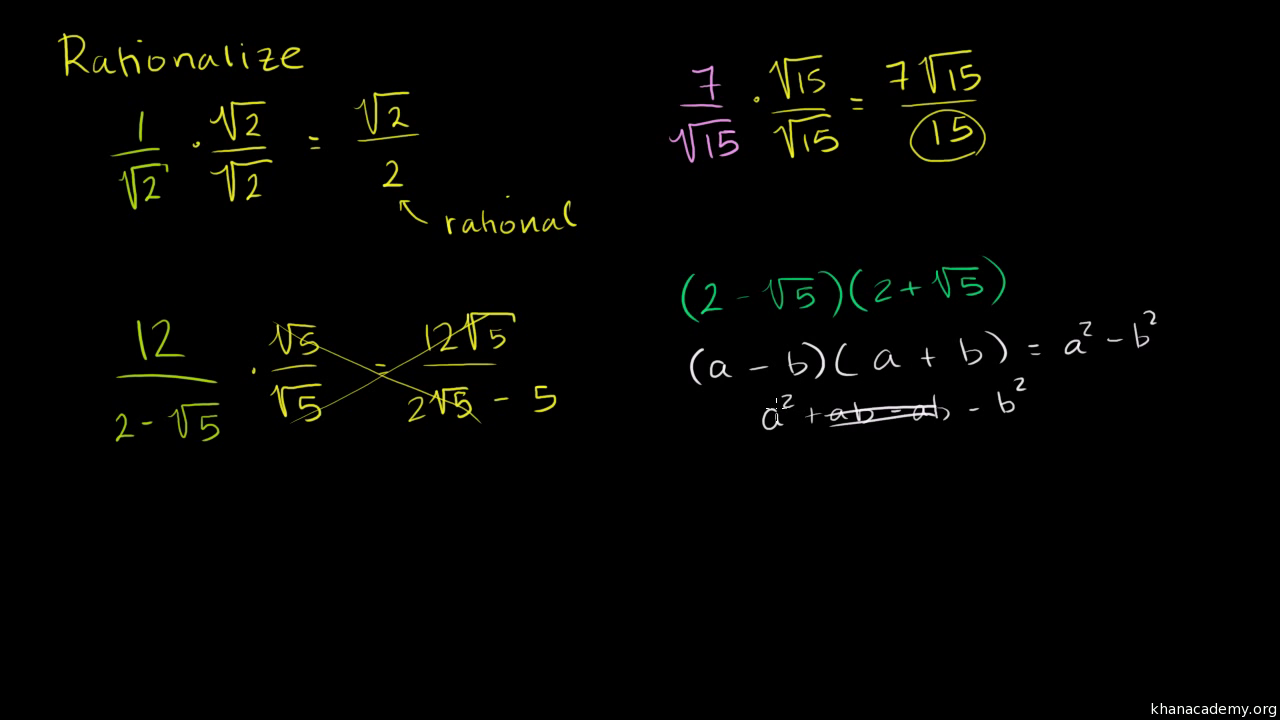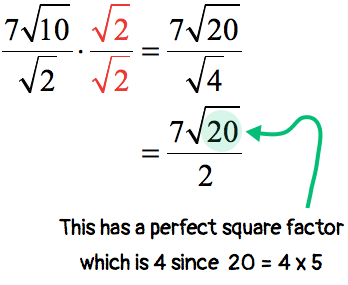Fantastic Info About How To Get Rid Of A Square Root In The Denominator
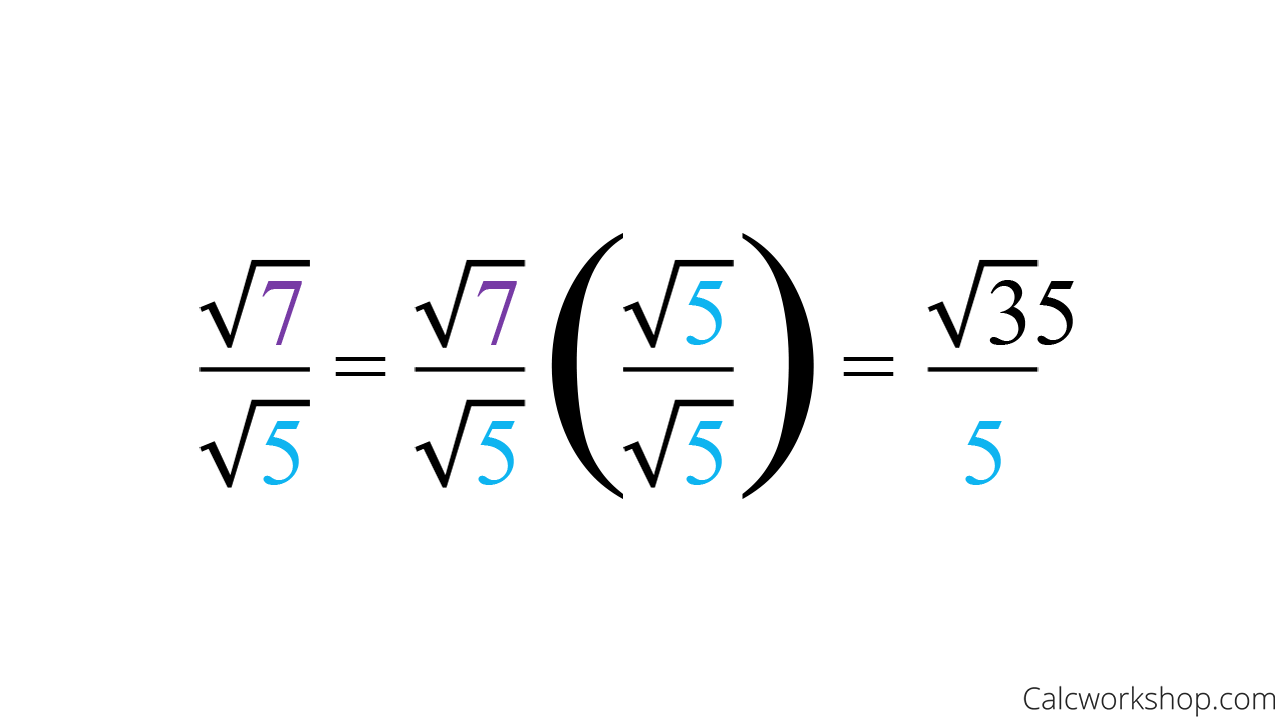
Now the denominator has a rational number (=2).
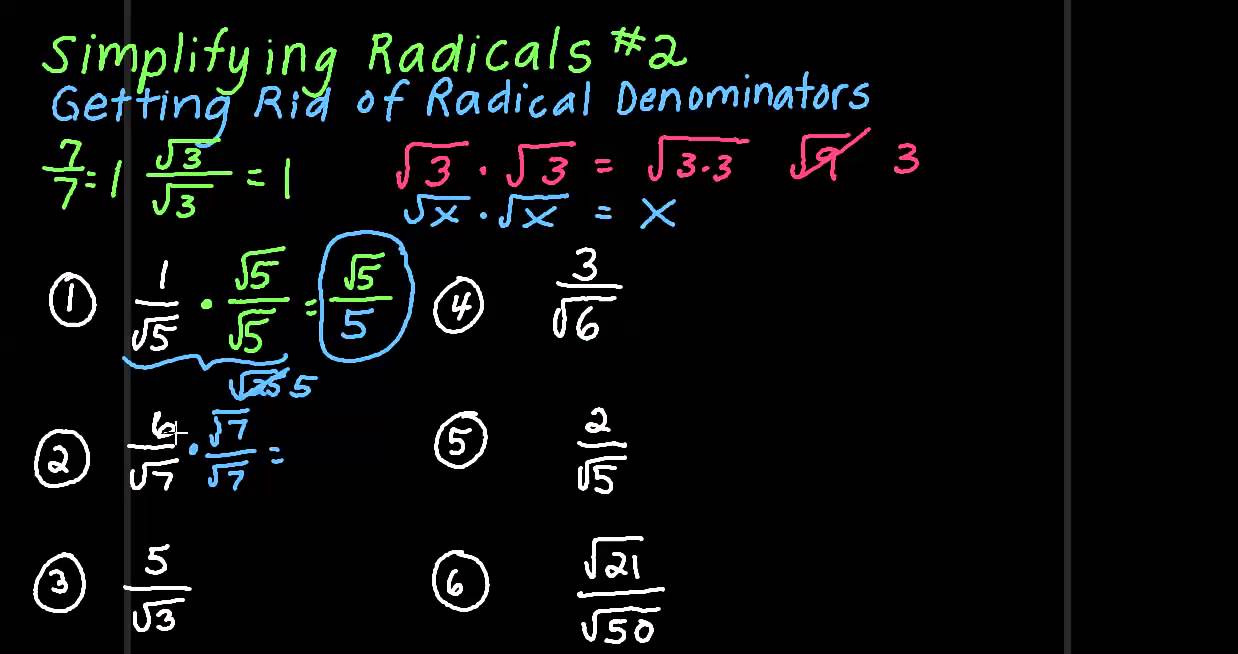
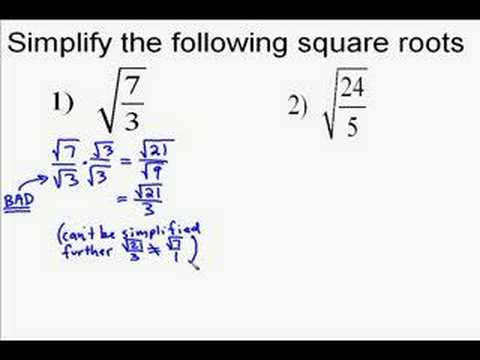
How to get rid of a square root in the denominator. Since the denominator is a binomial in which one of the terms is a square root, we need to multiply the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the binomial in order to. The denominator contains a radical expression, the square root of 2. So because the exponent term in the example is a cube or third power, you must apply a cube root or third.
Delete the radical at the bottom by multiplying for sã è is sqrt 2 from sqrt 2 cdot sqrt 2 = sqrt 4 = 2. Multiply tiptop and bottom by the square root of 2, because: Information technology is ok to have an.
Thursday 28th of dec 20:26. In the first exercise he removes the square roots from the numerator, in the second he removes it from. 3 / root (5) = 3.
With a bit more clear information about get rid of square roots in a fraction, i will be able to help you if i knew. Rationalizing expressions with one radical in the denominator is easy. You can do this by multiplying the top and bottom of.
When we have a fraction with a root in the denominator, like 1/√2, it’s often desirable to manipulate it so the denominator. For example, with a square root, you just need to get rid of the square root. Conjugate multiplication rationalizes the numerator or denominator of a fraction, which means getting rid of square roots.
Multiply the numerator and denominator by the. Multiply the numerator and denominator by the square root, for example. Also i have a picture here of two different exercises which i totally don't understand.
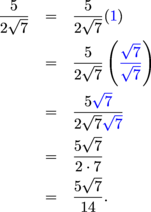
In this case, to get rid of the square root in the denominator, you multiply both numerator and denominator by the square root of 5, with the following result: On the left side of the equation, the square root of (x + 2/3) 2 is simply x + 2/3. 51.84 = (51.84 ⋅ 100) / 100.
Get the answers you need, now! Rationalize the denominator cube root calculator. You cannot have square roots in the denominator of an equation.
If the denominator has a square root, then get rid of it. To clear a square root on the denominator. √2 × √2 = 2:
You need to multiply so the square root goes away.